What is Big Data? Surfing the web, using social networks, watching a video, carrying out a bank transaction, etcetera. Nowadays, the capacity to generate data is such that a smartphone had more processing capacity than NASA’s technology when the first human being was sent to the moon. We are only talking at the user level. The rise of the internet of things (IoT) is causing more and more devices to be constantly sending data from their sensors. It is estimated that this year there may be more than two hundred billion connected objects, which is why Big Data is so necessary.
Nowadays, billions of bytes of information are generated every day. The combination of large amounts of data, powerful analysis tools, modern algorithms and artificial intelligence, together with the low cost of storing such data, make this the era of Big Data, the era where data is a real gold mine.
What is Big Data?
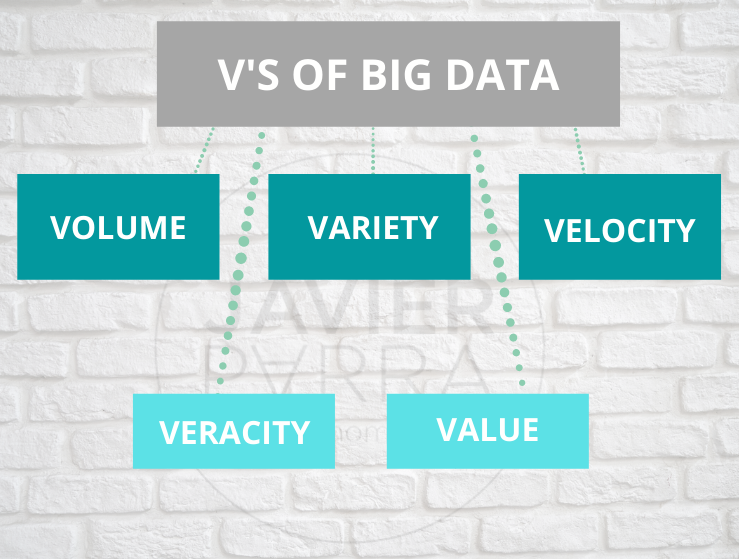
To know what Big Data is, we must understand that this term arose to refer to manipulating a large amount of data. In other words, it refers to a quantity of data with such a level of volume and complexity that it cannot be processed by conventional software. The characteristics of Big data are reflected around its so-called 3 V’s:
- Massive volume of data.
- Variety of origin of the information.
- The speed with which the information is received, transformed and manipulated.
Nowadays, the number of V’s has increased by adding, for example, veracity, which brings with it the ability to extract quality data and leave aside those that are more unpredictable and valuable, i.e. the importance of bringing to light data that is relevant for each specific use and being able to make it profitable. Today, many organisations analyse data and use it to improve decision-making and generate a lot of value for their customers using their own information.
With so much information available, it has become essential to capture, store, analyse, classify, categorise and manipulate it for use by businesses, organisations and even governments.
There are 4 dimensions of analysis that allow the achievement of the main benefits of Big Data, and they are:
- Descriptive analysis: which explains what is happening.
- Diagnostic analysis: which explains why something is happening.
- Predictive analytics: which analyses or anticipates a likely outcome.
- Prescriptive analytics: which pinpoints how to make something happen.
Applications of Big Data
Almost everything we do at home, at work, in our free time, etc., produces data that companies collect, analyse and use, powered by devices that connect to the Internet.
1. Big data in commerce
Retail is an excellent field for Big Data. Supermarkets, for example, can analyse information in real-time, which allows them to solve inventory problems, organise products according to their customers’ consumption habits, organise prices, and so on.
Some sportswear brands place sensors in their garments capable of capturing barometric data, heart rate and calories consumed by the user to offer optimised exercise programmes for each customer.
Big Data is also applied to shop counters, with many retailers assessing the reaction of passers-by to their window displays to evaluate the likelihood of them entering the shop depending on what the shop is displaying.
Online shops are no exception in using Big Data as they can capture every interaction of their visitors and from those interactions offer them in real-time what they are looking for, thanks to the ability to test algorithms and sales impact analysis.
Restaurants also use data to set their menus, order their menu, offer promotions, and so on. All this according to their consumers’ preferences, but not only limited to food, ranging from the wine offer to the positions of the tables.
2. Big Data in entertainment
Entertainment companies use their customers’ data to recommend series, films and documentaries that interest them based on their preferences. In the same way, they use the enormous amount of data they collect to develop new productions taking into account their audience’s favourite genre, favourite actors, etc., ensuring that millions see their productions of people worldwide.
In print media, natural language generation platforms exist to produce their stories (blog posts, news, and even recipes), and most people would never imagine that an algorithm produces these stories.
Disney uses sensors to capture data on its millions of visitors, their movements in the parks, how long they wait for rides, and even what they eat and drink.
Casinos collect data to maximise customer spending, assessing each customer to prevent cheating, detect card counters, and so on.
3. Big Data in science
A clear example is the European Organization for Nuclear Research or better known by its acronym CERN, imagine without the use of Big Data having to analyse the massive amounts of data generated by the Large Hadron Collider, it would be something titanic if not almost impossible. Only modern computers and the sophisticated algorithms we have today can efficiently handle such amounts of data at speed they need to analyse.
In nature conservation, predictive analytics, sensors and satellites allow our scientists to track endangered plants and animals, assess the progress of ozone depletion, the impact of humans on natural ecosystems, and even reach new, unexplored areas in the deep ocean. Seismographs use predictive modelling and algorithms to analyse data from sensors, atmospheric conditions, historical data, photos, etc., to predict earthquakes with 90% accuracy.
4. Big Data in technology
This is by far the area that leads the implementation of Big Data. Social networks have incalculable amounts of information from their users. Their preferences and tastes are detailed; thanks to this, those who want to advertise a product can have detailed information to the millimetre of its target audience.
IBM’s Watson continuously learns by processing huge amounts of data through algorithms, which are then used to diagnose financial markets, early diagnosis of cancer and crime prevention.
Google is the ultimate data producer and collector, processing exabytes of information in real-time to stay at the top of the online search engines.
5. Big Data in manufacturing
Embedded microchips and sensors can capture data from machines and equipment to predict what maintenance needs to be done before breakdowns occur and use the information generated by their machinery to deliver information to users in the industrial sector.
Big Data has become a fundamental element in the world of information technology as all the information it provides is transformed into accurate decisions at the right time. Today, data is used to determine what happened. Still, it is also advantageous to determine what is happening in real-time, giving direction to marketing, reducing costs, improving services and saving time.








